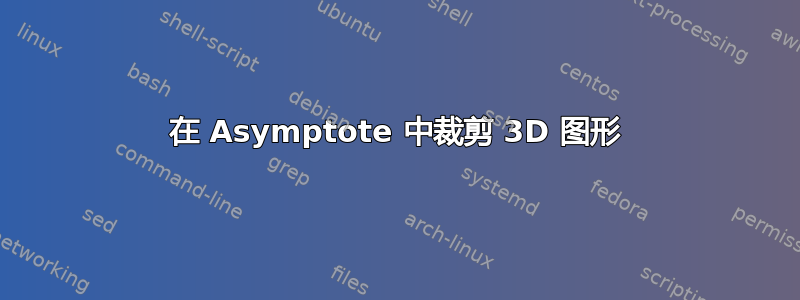
我想在平面 z=1 处裁剪下面的 3D 图形。我尝试使用limits((-1,-1,0),(1,1,1),Crop);,但这只会删除我的框架。

\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{asymptote}
\begin{document}
\begin{asy}[width=0.5\linewidth]
import graph3;
size(200,200,IgnoreAspect);
currentprojection=perspective(4,2,3);
real f(pair z) {return sqrt(4*(z.x)^2+(z.y)^2);}
draw(surface(f,(-1,-1),(1,1),nx=30,Spline),green+opacity(0.4),render(merge=true));
limits((-1,-1,0),(1,1,1),Crop);
xaxis3("$x$",Bounds,InTicks);
yaxis3("$y$",Bounds,InTicks(beginlabel=false));
zaxis3("$z$",Bounds,InTicks);
\end{asy}
\end{document}
注意:我确信我可以通过缩放圆锥体来得到我想要的图形,但我也希望能够在其他情况下裁剪 f(x,y) 的图形。我知道这个问题如何在 Asymptote 中将一个曲面与另一个曲面相交处切割?,但它的答案是不够的,我猜想存在一种更简单的方法。
答案1
事实证明,有一种更好的方法可以做到这一点,尽管这种方法相当耗费内存。首先,将以下代码保存在名为的文件中crop3D.asy。此代码的灵感来自示例分割补丁程序。
import three;
/**********************************************/
/* Code for splitting surfaces: */
struct possibleInt {
int value;
bool holds;
}
int operator cast(possibleInt i) { return i.value; }
surface[] divide(surface s, int region(triple), int numregions,
bool keepregion(int) = null) {
int defaultdepth = 17;
if (keepregion == null) keepregion = new bool(int region) {
return (0 <= region && region < numregions);
};
surface[] toreturn = new surface[numregions];
for (int i = 0; i < numregions; ++i)
toreturn[i] = new surface;
possibleInt region(patch P) {
triple[][] controlpoints = P.P;
possibleInt theRegion;
theRegion.value = region(controlpoints[0][0]);
theRegion.holds = true;
for (triple[] ta : controlpoints) {
for (triple t : ta) {
if (region(t) != theRegion.value) {
theRegion.holds = false;
break;
}
}
if (!theRegion.holds) break;
}
return theRegion;
}
void addPatch(patch P, int region) {
if (keepregion(region)) toreturn[region].push(P);
}
void divide(patch P, int depth) {
if (depth == 0) {
addPatch(P, region(P.point(1/2,1/2)));
return;
}
possibleInt region = region(P);
if (region.holds) {
addPatch(P, region);
return;
}
// Choose the splitting function based on the parity of the recursion depth.
triple[][][] Split(triple[][] P) {
if (depth % 2 == 0) return hsplit(P);
else return vsplit(P);
}
patch[] Split(patch P) {
triple[][][] patches = Split(P.P);
return sequence(new patch(int i) {return patch(patches[i]);}, patches.length);
}
patch[] patches = Split(P);
for (patch PP : patches)
divide(PP, depth-1);
}
for (patch P : s.s)
divide(P, defaultdepth);
return toreturn;
}
/**************************************************/
/* Code for cropping surfaces */
// Return 0 iff the point lies in box(a,b).
int region(triple pt, triple a=O, triple b=(1,1,1)) {
real x=pt.x, y=pt.y, z=pt.z;
int toreturn=0;
real xmin=a.x, xmax=b.x, ymin = a.y, ymax=b.y, zmin=a.z, zmax=b.z;
if (xmin > xmax) { xmin = b.x; xmax = a.x; }
if (ymin > ymax) { ymin = b.y; ymax = a.y; }
if (zmin > zmax) { zmin = b.z; zmax = a.z; }
if (x < xmin) --toreturn;
else if (x > xmax) ++toreturn;
toreturn *= 2;
if (y < ymin) --toreturn;
else if (y > ymax) ++toreturn;
toreturn *= 2;
if (z < zmin) --toreturn;
else if (z > zmax) ++toreturn;
return toreturn;
}
bool keepregion(int region) { return (region == 0); }
// Crop the surface to box(a,b).
surface crop(surface s, triple a, triple b) {
int region(triple pt) {
return region(pt, a, b);
}
return divide(s, region=region, numregions=1, keepregion=keepregion)[0];
}
然后将以下内容保存foo.asy在同一目录中:
settings.outformat="png";
settings.render=16;
import crop3D;
import graph3;
size(390pt/2, IgnoreAspect); //390pt is the default text width for the article class
currentprojection=perspective(4,2,3);
real f(pair z) {return sqrt(4*(z.x)^2+(z.y)^2);}
surface s = surface(f,(-1,-1),(1,1),nx=30,Spline);
s = crop(s, (-1,-1,-1),(1,1,1));
draw(s, green+opacity(0.4), render(merge=true));
xaxis3("$x$",Bounds,InTicks);
yaxis3("$y$",Bounds,InTicks(beginlabel=false));
zaxis3("$z$",Bounds,InTicks);
然后在命令行中输入以下内容进行编译asy foo。最终你应该得到一个foo.png如下所示的文件:

答案2
据我所知, Asymptote 为您的一般问题提供的最接近的解决方案是一个可选参数(输出的函数bool),它允许您丢弃不需要的补丁:
\documentclass[margin=10pt]{standalone}
\usepackage{asymptote}
\begin{document}
\begin{asy}
import graph3;
size(390pt/2, IgnoreAspect); //390pt is the default text width for the article class
currentprojection=perspective(4,2,3);
real f(pair z) {return sqrt(4*(z.x)^2+(z.y)^2);}
bool allow(pair z) {return f(z) <= 1;}
surface conegraph = surface(f,(-1,-1),(1,1),nx=100,Spline,allow);
draw(conegraph,green+opacity(0.4),render(merge=true));
xaxis3("$x$",Bounds,InTicks);
yaxis3("$y$",Bounds,InTicks(beginlabel=false));
zaxis3("$z$",Bounds,InTicks);
\end{asy}
\end{document}
不幸的是,这种解决方案并不令人满意,因为它往往会产生锯齿状边缘:

因此,我一般的建议是重新参数化;这对于这个特定的函数尤其适用,因为这个Spline选项只适用于可微分函数。(如果你仔细观察,你会发现图上的“点”有点太圆了。)有关此问题的示例,请参阅问题


